实验二 进程控制
“16281052 杨涵晨 计科1601 ”
一.实验目的
- 加深对进程概念的理解,明确进程和程序的区别。
- 掌握Linux系统中的进程创建,管理和删除等操作。
- 熟悉使用Linux下的命令和工具,如man, find, grep, whereis, ps, pgrep, kill, ptree, top, vim, gcc,gdb, 管道等。
二.实验题目
- 打开一个vi进程。通过ps命令以及选择合适的参数,只显示名字为vi的进程。寻找vi进程的父进程,直到init进程为止。记录过程中所有进程的ID和父进程ID。将得到的进程树和由pstree命令的得到的进程树进行比较。
- 编写程序,首先使用fork系统调用,创建子进程。在父进程中继续执行空循环操作;在子进程中调用exec打开vi编辑器。然后在另外一个终端中,通过ps –Al命令、ps aux或者top等命令,查看vi进程及其父进程的运行状态,理解每个参数所表达的意义。选择合适的命令参数,对所有进程按照cpu占用率排序。
- 使用fork系统调用,创建如下进程树,并使每个进程输出自己的ID和父进程的ID。观察进程的执行顺序和运行状态的变化。

- 修改上述进程树中的进程,使得所有进程都循环输出自己的ID和父进程的ID。然后终止p2进程(分别采用kill -9 、自己正常退出exit()、段错误退出),观察p1、p3、p4、p5进程的运行状态和其他相关参数有何改变。
三.实验解答
TASK 1
实验步骤
-
打开一个vi进程,同时使用另一个终端进行进程查询,使用 ps 指令
1 2 3
ps - auxc | grep vi$ # -auxc 显示所以进程 # grep program_filter_word 这里是vi 也可以是java c等来区分

-
寻找vi的父进程
利用ps -eo 指令进行查询
1 2 3 4
ps -eo pid,ppid,user,command | grep -w ^.<pid> # -eo 以指定格式输出 # pid 进程号,ppid 父进程号, user 用户,command 指令 # grep 指定指令
依次进程回溯查询我们可以得到如下所示进行树的一条链.
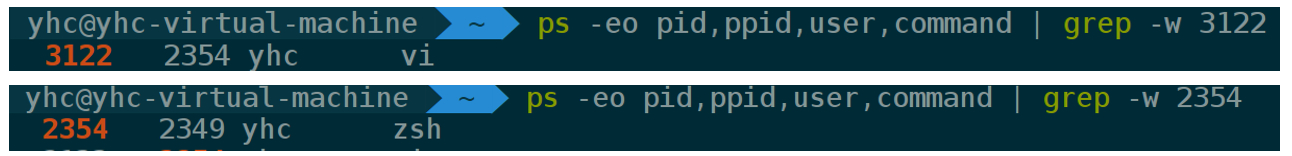
1 -> 901 ->1033 ->1076->2349->2354->3122
-
通过pstree进行部分查询,可以得到如下进程树,发现和我的是一致的
1 2
pstree 2349 # pstree -pid 以pid为根的子树
实验总结
- ps 指令十分灵活,参数也很多,功能十分强大
- pstree 指令可以为我们构建一个完成的进程树,也可以将部分子树进行输出
TASK 2
实验步骤
-
编写程序 fork_2.c
其中利用fork()函数创建两个相同的进程
神奇的是:fork()函数会返回两次,一次为子进程ID,一次为0。
利用execl() 进行linux的命令调用
先声明:int execl(const char* path,const char* arg,…); eg : execl(“/bin/ls”,”ls”,”-l”,”/home”,(char*)0);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
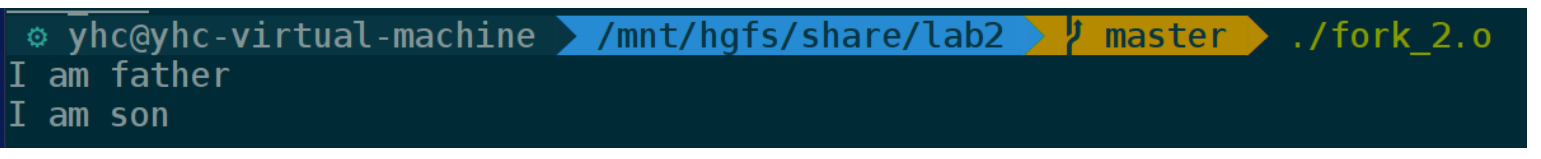
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> int execl(const char* path,const char* arg,...); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { pid_t pid; pid = fork(); if( pid < 0 ){ // 没有创建成功 perror("fork create error"); } if(0 == pid){ // 子进程 printf("I am son\n"); int ret; ret = execl("/usr/bin/vi","vi","text.txt",(char*)0); if (ret == -1) { perror ("execl"); } }else if(pid > 0){ // 父进程 printf("I am father\n"); while(1){ sleep(1); } } return 0; }
-
编译可执行文件fork_2.o
1
gcc fork_2.c -o fork_2.o -Wall
-
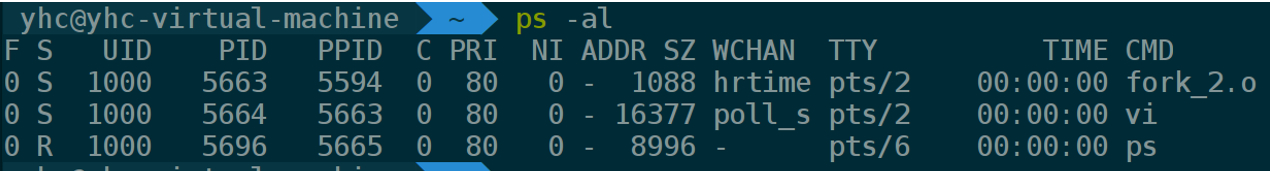
利用ps -al指令进行查看进程
父进程5663利用fork函数,创建一个子进程5664,5664进程调用vi指令
-
执行结果
实验总结
-
fork() 函数是为父进程创建一个只有pid等部分结构不同的子进程,直接复制PCB等

父进程执行Part A — Part.B 子进程只执行Part.B
-
利用execl() 进行linux的命令调用时,一定要注意路径
TASK 3
实验步骤
-
编写实验代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int i = 0; pid_t fpid,ppid; //pid指当前进程的pid, //fpid指fork返回给当前进程的值 ppid = getppid(); printf("the first node of tree‘s father %d\n",ppid); for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) { fpid = fork(); if (fpid == 0) { // printf("%d child %4d %4d %4d\n", i, getppid(), getpid(), fpid); } else{ printf("%d parent %4d %4d\n", i, getpid(), fpid); } if (i == 1 && fpid != 0 && ppid != getppid()) { fpid = fork(); if (fpid == 0) { // printf("%d child %4d %4d %4d\n", i, getppid(), getpid(), fpid); } else{ printf("%d parent %4d %4d\n", i, getpid(), fpid); } } } return 0; }
实验代码解释:
- 利用for循环进行三次fork产生3个子节点
- 利用if 判断条件,只在子节点上再产生一个子子节点
-
实验结果

TASK 4
实验步骤
1.1利用kill -9 进行进程终止
-
编写代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) { int i = 0; pid_t fpid,ppid; //pid指当前进程的pid, //fpid指fork返回给当前进程的值 ppid = getppid(); printf("the first node of tree‘s father %d\n",ppid); for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) { fpid = fork(); if (fpid == 0) { // printf("%d child %4d %4d %4d\n", i, getppid(), getpid(), fpid); } else{ printf("%d parent %4d %4d\n", i, getpid(), fpid); } if (i == 1 && fpid != 0 && ppid != getppid()) { fpid = fork(); if (fpid == 0) { // printf("%d child %4d %4d %4d\n", i, getppid(), getpid(), fpid); } else{ printf("%d parent %4d %4d\n", i,getpid(), fpid); } } } while(1) { sleep(3); printf("%4d parent %4d\n", getppid(), getpid()); } return 0; }
利用 ps - al 进行查看

可以看到只有p2死亡,而它的子进程p4,p5还存在,但是父节点变化了
1.2利用exit()函数终止
-
修改编写程序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
i = 10; while(i-->0) { printf("%4d parent %4d\n", getppid(), getpid()); sleep(3); if(ppid2+1 == getpid()&&i<7) { exit(1); } }
-
exit()函数退出

可以看到,p2的退出没有影响到它的子进程,p4,p5的父进程的也被改变。
1.3利用段错误终止
-
修改编写程序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
i = 10; while(i-->0) { printf("%4d parent %4d\n", getppid(), getpid()); sleep(3); if(ppid2 +1 == getpid()&&i<7) { int *ptr = NULL; *ptr = 0; } }
-
段错误退出时

可以看到,p2的退出没有影响到它的子进程,p4,p5的父进程的也被改变。