机器学习experiment_GAP_LeNet_MMD
‘”tensorflow + torch “
1. 实验目标
- 直观观察不同类中的差距
- 利用MMD进行差距度量
2. 实验环境

数据集:MNIST cluttered dataset
1
2
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
jupyter notebook mnist.py # The heatmaps are available in out/
原始数据:

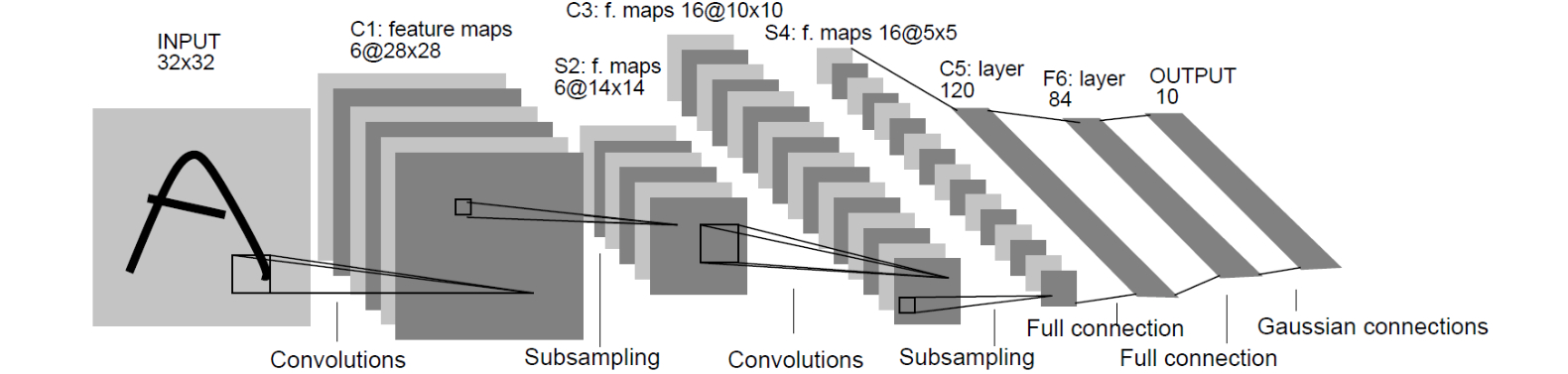
网络结构:
3. 实验步骤
- tensorflow 网络搭建:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
slim = tf.contrib.slim
def le_net(images, num_classes=10, scope='LeNet'):
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'LeNet', [images, num_classes]):
net = slim.conv2d(images, 32, [5, 5], scope='conv1')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], 2, scope='pool1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [5, 5], scope='conv2')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], 2, scope='pool2')
gap = tf.reduce_mean(net, (1, 2))
with tf.variable_scope('GAP'):
gap_w = tf.get_variable('W', shape=[64, 10], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.01))
logits = tf.matmul(gap, gap_w)
return logits, net, gap
- 迭代运行:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
for i in range(step_start, 100000):
print(i)
batch_xs, batch_ys, _ = next_batch(images_train, labels_train, i, batch_size)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
if i % 10 == 0:
save(sess, saver, i)
accuracy_list = []
j = 0
while True:
batch_xt, batch_yt, reset = next_batch(images_test, labels_test, j, b atch_size, debug=False)
if reset:
break
accuracy_list.append(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: batch_xt, y_: batch_yt}))
j += 1
print('steps =', i * batch_size, 'mean accuracy =', np.mean(accuracy_list))
inspect_class_activation_map(sess, class_activation_map, top_conv, images_test,labels_test, i, 50, x, y_, y)
break;
- GAP 值导入 pandas 库
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
GAP = np.load('GAP_Value_10*300*64.npy')
GAP = Normalize(GAP)
result = []
x = 2
y = 1
for i in range(10):
result.append([])
for i in range(10):
A = []
A = GAP[i][y:x+y]
for j in range(10):
B = []
B = GAP[j][x+y:2*x+y]
X = torch.Tensor(A)
Y = torch.Tensor(B)
X,Y = Variable(X), Variable(Y)
result[i].append(float(mmd_rbf(X,Y)))
- MMD函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
def mmd_rbf(source, target, kernel_mul=2.0, kernel_num=5, fix_sigma=None):
'''
计算源域数据和目标域数据的MMD距离
Params:
source: 源域数据(n * len(x))
target: 目标域数据(m * len(y))
kernel_mul:
kernel_num: 取不同高斯核的数量
fix_sigma: 不同高斯核的sigma值
Return:
loss: MMD loss
'''
batch_size = int(source.size()[0])#一般默认为源域和目标域的batchsize相同
kernels = guassian_kernel(source, target,
kernel_mul=kernel_mul, kernel_num=kernel_num, fix_sigma=fix_sigma)
#根据式(3)将核矩阵分成4部分
XX = kernels[:batch_size, :batch_size]
YY = kernels[batch_size:, batch_size:]
XY = kernels[:batch_size, batch_size:]
YX = kernels[batch_size:, :batch_size]
loss = torch.mean(XX + YY - XY -YX)
return loss#因为一般都是n==m,所以L矩阵一般不加入计算
4. 实验结果
4. 1 CAM 结果

4.2 MMD on GAP
10x64 同类 <=1
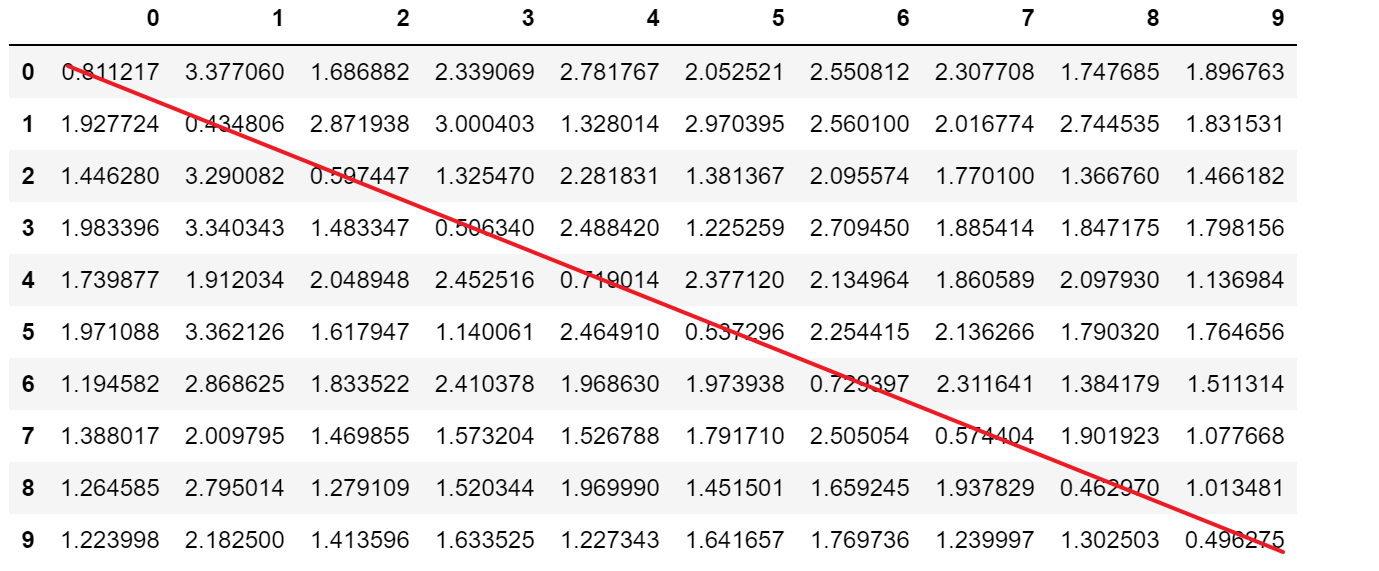
1 vs 1 之间比较,出现问题