深度学习中的Model定义和Train函数

1. 官方网络结构
这里我们主要使用tensorflow官方中的slim模块中的net网络进行训练,利用训练好的预参数进行finetune
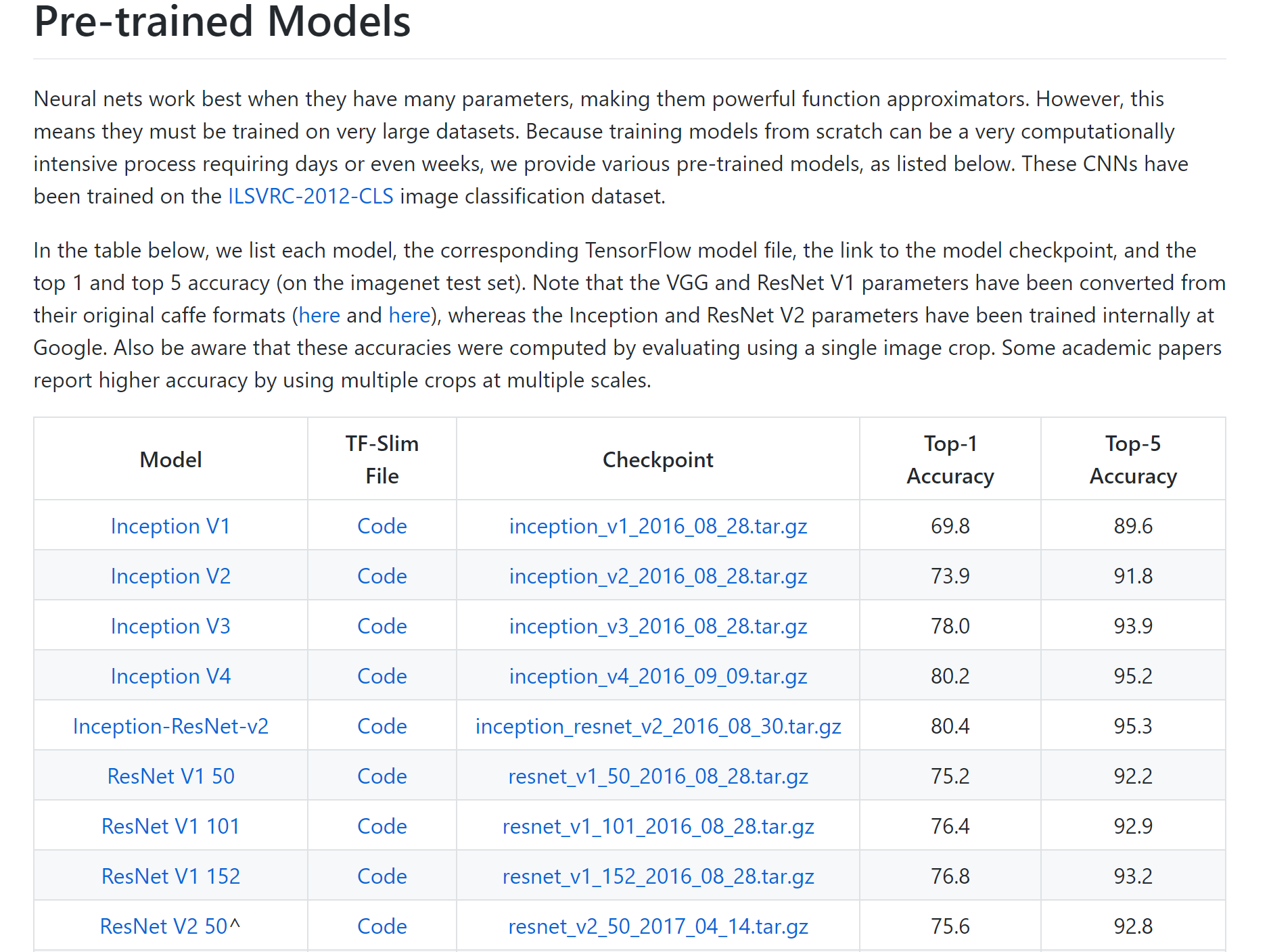
2. Model 定义
开始编写Model.py文件,利用slim模块的net进行对应的模型搭建,包括定义loss,accaury以及优化算法的设计
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class Model(object):
def __init__(self, is_training,
num_classes=2,
fixed_resize_side=256,
default_image_size=224):
# model 模型初始化,传入的参数类型
self._num_classes = num_classes
self._is_training = is_training
self._fixed_resize_side = fixed_resize_side
self._default_image_size = default_image_size
主要函数
-
对传入的图像进行预处理,主要调用processing.py 中的各种方法进行处理
def preprocess(self, inputs) -
预测函数,输入预处理后的数据,然后经过网络模型后得到输出值
def predict(self, preprocessed_inputs) -
得到输出值后,将输入值进行后续处理,进行softmax等等操作
def postprocess(self, prediction_dict) -
根据输出值计算loss这里的分类问题使用交叉熵
def loss(self, prediction_dict, groundtruth_lists) -
计算accuracy
def accuracy(self, postprocessed_dict, groundtruth_lists)
主要看一下predict函数
使用了slim模块中的net,resnet_v1网络,我们也可以使用对应的其他网络结构
但是resnet_50是一个2000分类网络,我们需要修改最后的输出层,利用一个全连接将2000变成我们所需要的num_classes,所以参数中的num_classes = None是必须的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
def predict(self, preprocessed_inputs):
"""Predict prediction tensors from inputs tensor.
输入 [batch_size,height, width, num_channels] a batch of images.
利用slim模块加载预训练模型,然后返回softmax之前的参数
输出 结果值{'logits': logits}
"""
# resnet_v1_50 函数返回的形状为 [None, 1, 1, num]
with slim.arg_scope(nets.resnet_v1.resnet_arg_scope()):
net, endpoints = nets.resnet_v1.resnet_v1_50(
preprocessed_inputs, num_classes=None,
is_training=self._is_training)
#conv5 = endpoints['resnet/conv5']
# 为了输入到全连接层,需要用函数 tf.squeeze 去掉形状为 1 的第 1,2 个索引维度。
net = tf.squeeze(net, axis=[1, 2])
# 将resnet的最后一层输出进行处理,变成二分类
logits = slim.fully_connected(net, num_outputs=self.num_classes,
activation_fn=None,
scope='Predict/logits')
return {'logits': logits}
也可以利用endpoints获取前面几层的参数进行,后续操作
后续我们可以通过这些值来计算conv后面的GAP的值
3. Train 核心实现
train.py 文件中的函数就比较多了,这里就不一一列举
我们不只使用了tf.slim模块的还使用了 tf.estimator.Estimator
3.1 Estimator简介
这个接口就是为了方便模型的训练过程而开发的,它可以同时训练和验证模型,让训练过程更简单可控。
利用 tf.estimator 训练模型时需要写两个重要的函数,一个用于数据输入的函数(input_fn),另一个用于模型创建的函数(model_fn)。下面逐一来说明。(这里沿用以前文章 ,数据格式仍然采用 TFRecord)。
首先我们从调用顺序来介绍一下大概的训练过程(完整官方文档:tf.estimator):
- 使用
tf.estimator.train_and_evaluate启动训练和验证过程。该函数的完整形式是:
1
tf.estimator.train_and_evaluate(estimator, train_spec, eval_spec)
其中 estimator 是一个 tf.estimator.Estimator 对象,用于指定模型函数以及其它相关参数;train_spec 是一个 tf.estimator.TrainSpec 对象,用于指定训练的输入函数以及其它参数;eval_spec 是一个 tf.estimator.EvalSpec 对象,用于指定验证的输入函数以及其它参数。这三个分别有对应的对象生成函数,我们需要对这三个对象进行实例化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
estimator = tf.estimator.Estimator(model_fn=create_model_fn,
model_dir=FLAGS.model_dir)
train_input_fn = create_input_fn([FLAGS.train_record_path],
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size)
train_spec = tf.estimator.TrainSpec(input_fn=train_input_fn,
max_steps=FLAGS.num_steps)
eval_input_fn = create_input_fn([FLAGS.val_record_path],
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size,
num_epochs=1)
predict_input_fn = create_predict_input_fn()
eval_exporter = tf.estimator.FinalExporter(
name='servo', serving_input_receiver_fn=predict_input_fn)
eval_spec = tf.estimator.EvalSpec(input_fn=eval_input_fn, steps=None,
exporters=eval_exporter)
tf.estimator.train_and_evaluate(estimator, train_spec, eval_spec)
其中model_fn 是这个实例化对象的输入数据,但是是以函数形式传入的
先来看model_fn, 由于过于复杂,我直接参考的官方源码,复制粘贴的,解释都在代码里面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
def create_model_fn(features, labels, mode, params=None):
"""Constructs the classification model.
Modifed from:
https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/
object_detection/model_lib.py.
Args:
features: A 4-D float32 tensor with shape [batch_size, height,
width, channels] representing a batch of images. (Support dict)
labels: A 1-D int32 tensor with shape [batch_size] representing
the labels of each image. (Support dict)
mode: Mode key for tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
params: Parameter dictionary passed from the estimator.
Returns:
An `EstimatorSpec` the encapsulates the model and its serving
configurations.
"""
# 定义网络参数
params = params or {}
# 定义网络衡量参数
loss, acc, train_op, export_outputs = None, None, None, None
# 根据mode传参进行匹配,mode 指定训练模式,可以取 (TRAIN, EVAL, PREDICT)三者之一
is_training = mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN
# 根据传入的feature读取图片数据
cls_model = model.Model(is_training=is_training,
num_classes=FLAGS.num_classes)
#预处理,获得输出值,获得预测值
preprocessed_inputs = cls_model.preprocess(features.get('image'))
prediction_dict = cls_model.predict(preprocessed_inputs)
postprocessed_dict = cls_model.postprocess(prediction_dict)
# train
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN:
#进行对应预训练模型的加载
if FLAGS.checkpoint_path:
# checkpoint_exclude_scopes = 'resnet_v1_50/conv1,resnet_v1_50/block1'
# 指定一些层不加载参数
init_variables_from_checkpoint()
# not train
if mode in (tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN, tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL):
loss_dict = cls_model.loss(prediction_dict, labels)
loss = loss_dict['loss']
classes = postprocessed_dict['classes']
acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(classes, labels), 'float'))
tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss)
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', acc)
scaffold = None
# train
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN:
# 设定步数,设定学习率等等超参数
global_step = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
learning_rate = configure_learning_rate(FLAGS.decay_steps,
global_step)
optimizer = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate,
momentum=0.9)
# 冻结层设置,指定一些层不训练
# scopes_to_freeze = 'resnet_v1_50/block1,resnet_v1_50/block2/unit_1'
vars_to_train = get_trainable_variables()
train_op = slim.learning.create_train_op(loss, optimizer,
variables_to_train=vars_to_train,
summarize_gradients=True)
# 多少时间保存一次模型
keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours = FLAGS.keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours
saver = tf.train.Saver(
sharded=True,
keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours,
save_relative_paths=True)
tf.add_to_collection(tf.GraphKeys.SAVERS, saver)
scaffold = tf.train.Scaffold(saver=saver)
eval_metric_ops = None
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL:
accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(labels=labels, predictions=classes)
eval_metric_ops = {'Accuracy': accuracy}
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT:
export_output = exporter._add_output_tensor_nodes(postprocessed_dict)
export_outputs = {
tf.saved_model.signature_constants.PREDICT_METHOD_NAME:
tf.estimator.export.PredictOutput(export_output)}
# 返回这个实例化对象
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode=mode,
predictions=prediction_dict,
loss=loss,
train_op=train_op,
eval_metric_ops=eval_metric_ops,
export_outputs=export_outputs,
scaffold=scaffold)
再利用input函数,对tfrecord数据进行处理,并且引入并行化计算(无需知道底层实现)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
def create_input_fn(record_paths, batch_size=64,
num_epochs=0, num_parallel_batches=8,
num_prefetch_batches=2):
"""Create a train or eval `input` function for `Estimator`.
Args:
record_paths: A list contains the paths of tfrecords.
Returns:
`input_fn` for `Estimator` in TRAIN/EVAL mode.
"""
def _input_fn():
# 先实现decoder实例
decoder = get_decoder()
def decode(value):
keys = decoder.list_items()
tensors = decoder.decode(value)
# zip 将键值和value反过来
tensor_dict = dict(zip(keys, tensors))
image = tensor_dict.get('image')
# 读图片进行处理
image = transform_data(image)
features_dict = {'image': image}
return features_dict, tensor_dict.get('label')
dataset = read_dataset(
functools.partial(tf.data.TFRecordDataset,
buffer_size=8 * 1000 * 1000),
input_files=record_paths,
num_epochs=num_epochs)
if batch_size:
num_parallel_calles = batch_size * num_parallel_batches
else:
num_parallel_calles = num_parallel_batches
dataset = dataset.map(decode, num_parallel_calls=num_parallel_calles)
if batch_size:
dataset = dataset.apply(
tf.contrib.data.batch_and_drop_remainder(batch_size))
dataset = dataset.prefetch(num_prefetch_batches)
return dataset
return _input_fn
返回的是一个tf.dataset值
4.读取TFrecord
设置tfrecord文件的解码器,对事前定义好的图片文件进行解码, 相当于一个单映射
根据tf.contrib.slim.tfexample_decoder中的对应进行解码(前面录入时进行设置的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
def get_decoder():
# 设置tfrecord文件的解码器,对事前定义好的图片文件进行解码
# 根据tf.contrib.slim.tfexample_decoder中的对应进行解码
keys_to_features = {
'image/encoded':
tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value=''),
'image/format':
tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value='jpeg'),
'image/class/label':
tf.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64, default_value=tf.zeros([1],
dtype=tf.int64))}
#把items(string)映射为ItemHandler实例
items_to_handlers = {
'image': slim.tfexample_decoder.Image(image_key='image/encoded',
format_key='image/format',
channels=3),
'label': slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor('image/class/label', shape=[])}
decoder = slim.tfexample_decoder.TFExampleDecoder(
keys_to_features, items_to_handlers)
return decoder
然后利用read_dataset()进行数据读入,并且指定shuffle进行随机混乱。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
def read_dataset(file_read_fun, input_files, num_readers=1, shuffle=False,
num_epochs=0, read_block_length=32, shuffle_buffer_size=2048):
"""
利用并行化技术进行图像数据的处理与读入
tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices() 创建实例
tf.data.TFRecordDataset(): 用来读取tfrecord文件,dataset中的每一个元素就是一个TFExample
"""
# Shard, shuffle, and read files
filenames = tf.gfile.Glob(input_files)
if num_readers > len(filenames):
num_readers = len(filenames)
tf.logging.warning('num_readers has been reduced to %d to match input '
'file shards.' % num_readers)
filename_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(filenames)
if shuffle:
filename_dataset = filename_dataset.shuffle(100)
elif num_readers > 1:
tf.logging.warning('`shuffle` is false, but the input data stream is '
'still slightly shuffled since `num_readers` > 1.')
# 根据epochs 数量进行重复
filename_dataset = filename_dataset.repeat(num_epochs or None)
records_dataset = filename_dataset.apply(
tf.contrib.data.parallel_interleave(
file_read_fun,
cycle_length=num_readers,
block_length=read_block_length,
sloppy=shuffle))
if shuffle:
records_dataset = records_dataset.shuffle(shuffle_buffer_size)
return records_dataset